Until recently, the promise of 5G-enabled remote surgery was constrained by distance and infrastructure, effective only within roughly 5,000 kilometers and reliant on stable terrestrial networks.
This limitation has now been dramatically overcome.
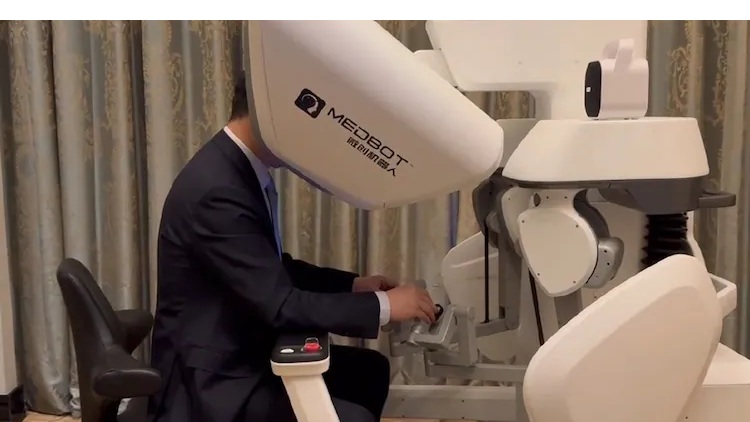
In a groundbreaking global first, on Monday, June 30, 2025, Chinese surgeons successfully performed robotic liver surgeries on patients located more than 5,000 kilometers away, using satellite communication instead of traditional ground-based internet.
This milestone ushers in a new era for medical care, particularly for patients in isolated, disaster-stricken, or conflict-ridden areas where connectivity is scarce or unreliable.
A Leap Forward in Medical Technology
Led by Professor Rong Liu of the PLA General Hospital, the surgical team conducted two complex robotic liver operations from Lhasa, Tibet, on patients situated in Beijing.
The procedures addressed serious conditions: one patient was battling liver cancer, while the other suffered from a benign hepatic tumor.
This achievement represents the first-ever telesurgery facilitated through satellite links.
This has effectively bypassed the need for local network infrastructure and opening the door to delivering expert surgical care virtually anywhere on the planet.
Overcoming the Latency Challenge
Satellite communication has traditionally been plagued by significant latency, delays often exceeding 600 milliseconds, which far surpasses the critical 200 milliseconds threshold necessary for the precision required in robotic surgery.
Excessive latency can cause dangerous lag between a surgeon’s commands and the robotic instruments’ responses, risking patient safety.
To conquer this, Prof. Liu’s team engineered three innovative solutions:
Adaptive Latency Compensation: Utilizing advanced neural networks, the system intelligently predicted the surgeon’s hand movements in real time.
This predictive capability limited errors in the robotic arms’ positioning to an astonishingly precise 0.32 millimeters, even when faced with high latency.
Dual-Link Redundancy: Recognizing the potential for satellite signal interruptions, the team implemented a backup 5G connection that could seamlessly take over within 280 milliseconds.
This fail-safe ensured that the surgery could be safely paused or continued without risk if the primary satellite link faltered.
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation: To optimize communication efficiency, the system prioritized critical control commands and high-definition video feeds, reducing bandwidth usage by 62% without compromising visual clarity.
This smart allocation was key to maintaining smooth, uninterrupted operation.
The Role of Apstar-6D Satellite
The surgeries were made possible by the Apstar-6D satellite, positioned approximately 36,000 kilometers above Earth in geostationary orbit.
This satellite provided a stable and reliable communication channel between the two cities, enabling the surgeons in Lhasa to remotely control robotic instruments with precision.
The two patients, aged 68 and 56, underwent surgeries lasting about two hours each.
Remarkably, both procedures resulted in minimal blood loss, only about 20 milliliters, and no complications were reported.
Thanks to the minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery and the precision enabled by the technology, both patients were discharged within 24 hours, underscoring the effectiveness and safety of this pioneering approach.
Expanding the Horizons of Surgery
This breakthrough shatters the previous 5,000-kilometer operational ceiling for remote surgery, extending the possible reach to over 150,000 kilometers, effectively anywhere on Earth and even beyond.
The implications are profound: expert surgical care can now be delivered to:
- frontline war zones,
- remote rural communities,
- disaster areas cut off from infrastructure, and even future space missions.
China is now poised to integrate this satellite-enabled remote surgery model into its mainstream healthcare system.
The vision is to create a scalable, space-powered medical network that can offer timely, high-quality surgical interventions regardless of geographic or infrastructural limitations.
A New Frontier for Global Healthcare
This pioneering feat not only demonstrates the power of combining 5G technology with satellite communications but also signals a transformative shift in how healthcare can be delivered worldwide.
By leveraging space-based infrastructure, medical expertise can be shared across continents instantly, saving lives and reducing healthcare disparities.
As this technology matures, it promises to revolutionize emergency response, routine surgeries, and chronic disease management in underserved areas.
The success of Prof. Liu’s team heralds a future where no patient is beyond the reach of skilled surgeons, no matter how remote their location.
In summary, the fusion of 5G and satellite technology has transcended previous boundaries, turning science fiction into reality.
This landmark achievement is a beacon of hope, illuminating the path toward a more connected, equitable, and resilient global healthcare system.